
当超导磁铁突然转变为正常状态(称为淬火)时,其线圈可能过热。磁铁通常包含淬火检测和保护系统,以实现更安全的操作。对于这些系统有效,重要的是要了解磁铁内发生的产生的电热瞬态现象。使用数值模拟,我们可以开发出更复杂的系统,以防止可能的破坏效果。
The Large Hadron Collider: The Most Powerful Particle Accelerator
由欧洲核研究组织(CERN)建造,大型强子对撞机(LHC)是具有许多记录的结构。它不仅是有史以来建造的最复杂的实验设施,也是存在的最大的单机器,而且目前也是世界上最大,最强大的粒子加速器。LHC有可能为各种与物理有关的问题提供答案。(采取虚拟旅游亲自看。)
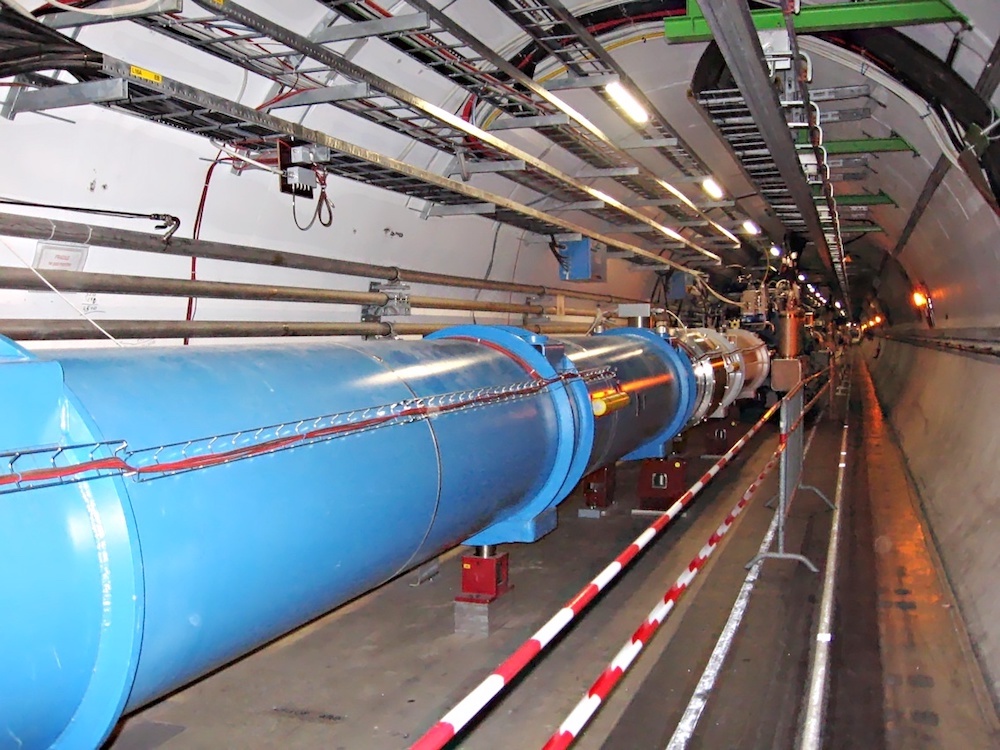
大型强子对撞机隧道的一部分。朱利安·赫尔佐格(Julian Herzog)的图像 - 自己的作品。获得许可CC BY-SA 3.0, 通过Wikimedia Commons。
加速器的操作后面是一个27公里的超导磁体和多个加速结构,可为颗粒增强能量。这些磁铁是由可以在超导状态下运行的线圈制成的,它保持了强的磁场,该磁场可引导颗粒梁周围围绕加速器环。
为了创建如此强大的田地,使用了用矩形电缆缠绕的铁饲养的电磁体。NB-TI丝嵌入铜基质中以形成链,然后将其扭曲并包裹在聚酰胺绝缘层中。当电缆冷却至1.9 K时,灯丝能够达到超导状态,进而使电缆携带更大的电流密度。
Left: Cross section of the magnet. Right: Cable layout. Images by L. Bortot, M. Maciejewski, M. Prioli, A.M. Fernandez Navarro, S. Schöps, I. Cortes Garcia, B. Auchmann, and A.P. Verweij and taken from their乐动滚球app下载Comsol会议2016慕尼黑论文。
When designing superconducting magnets like those in the LHC, it’s important to consider potential scenarios that could cause disruptive effects. One such example is quenches.
Studying Quenches in Superconducting Magnets
一种quenchrefers to the sudden transition of a magnet from the superconducting state to a normal state. This process occurs when the working point of a superconductor magnet moves out of what is called the关键空间, which then causes energy stored in the magnetic field to be released as Ohmic losses.
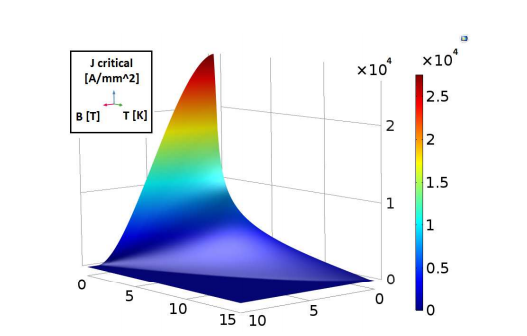
Plot of the critical surface for the filaments, with the maximum current density shown as a function of the magnetic and temperature fields. Image by L. Bortot, M. Maciejewski, M. Prioli, A.M. Fernandez Navarro, S. Schöps, I. Cortes Garcia, B. Auchmann, and A.P. Verweij and taken from their COMSOL Conference 2016 Munich paper.
发生淬火时,它会迫使传导电流从细丝到嵌入的铜基质。这种运动会导致磁铁内部的线圈过热。为了防止可能的破坏效果,磁铁设计通常包括淬火检测和保护系统。但是,确保这些系统的有效性需要了解磁体内发生的电热瞬态现象。
Recognizing this, a team of researchers from CERN simulated a quench event in a superconducting magnet, using a main dipole from the LHC as their point of analysis. Let’s see how the flexibility and functionality of the COMSOL Multiphysics® software helped them to simulate this complex design.
构建超导磁铁的电热模型
When modeling a superconducting magnet, one of the challenges is accounting for the number of half turns. For the main dipole of the LHC, this number is 320. Each of these half turns must be set up with its respective variables and operators in order to compute relevant quantities. This process is not only time consuming, but it is also prone to error.
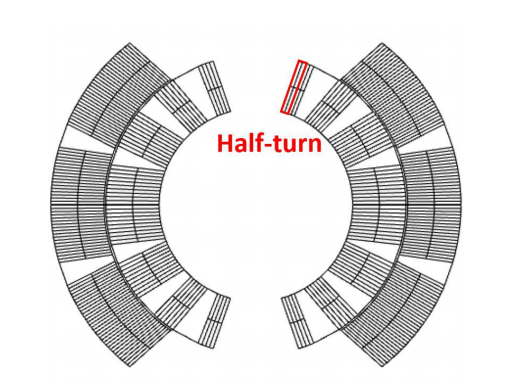
磁铁线圈的横截面,突出显示半回合。L. Bortot,M。Maciejewski,M。Prioli,A.M。图片Fernandez Navarro,S.Schöps,I。CortesGarcia,B。Auchmann和A.P. Verweij,从他们的Comsol Conference 2016慕尼黑论文中获乐动滚球app下载取。
为了加快模型创建过程并减少错误的机会,CERN的研究人员开发了一种自动化的Java®工作流,该工作流依赖于COMSOL API。该应用程序的结构基于三个主要功能层:
- 顶层,使用户能够描述带有文本输入文件的所需模型
- 中层,其中包括为API制定输入参数所需的数值方法
- Bottom layer, which offers classes to embed functionalities from the COMSOL API for use with Java®
有了这个工作流程,磁铁的半回合在具有索引功能的模型设计中实现。此功能非常有用,因为它允许您重新定义具有各个回合的公式的变量。因此,仅需要一个变量来描述共享同一属性的一组域。
Further, through the Java® workflow, the team at CERN was able to define various geometrical primitives, from points to lines, to construct their 2D model. Including model symmetries in the application helped to simplify the modeling process.
为了最大程度地减少网格节点的数量,因此,在模型网格中包括了非结构化和结构化元素的组合。为了确保结果的准确性,研究人员进行了网格灵敏度分析。
该模型中实施的物理学占超导电缆中诱导的非线性温度和田间依赖的材料特性和涡流。后者使团队能够计算淬火开始和传播。
两个时间依赖性研究的仿真结果
该分析包括两项连续执行的时间依赖性研究:
- The magnet’s current, linearly ramped up to the nominal value
- The exponential current decay, simulated at a time constant of 0.1 s
请注意,第二项研究将第一项研究的最终状态作为其初始状况。
研究人员首先在快速放电过程中研究了磁铁的行为。左侧的图显示了在标称条件下磁铁中的磁场。在100 a/s的线性坡道上,该田的变化会产生涡流。这些电流的等效磁化显示在右侧的图中。
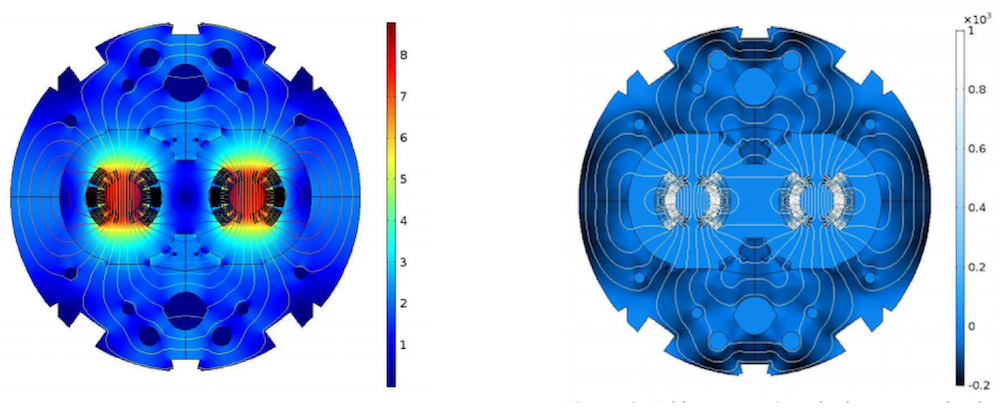
左:磁铁中的磁场在名义电流处。右:线性坡道在100 a/s的线性坡道期间的等效磁化。L. Bortot,M。Maciejewski,M。Prioli,A.M。的图像Fernandez Navarro,S.Schöps,I。CortesGarcia,B。Auchmann和A.P. Verweij,从他们的Comsol Conference 2016慕尼黑论文中获乐动滚球app下载取。
The losses that are generated impact the magnetic field, affecting the magnetic equivalent electrical impedance. They also deposit energy in the magnetic coil, dissipating some of the energy stored inside the magnetic field. If they are high enough, these losses can cause the temperature of the superconductor to rise beyond the critical surface. This can in turn cause the superconductor to transition to a normal state. At this stage, Ohmic losses are dominant in causing the magnet’s coil to heat up. The temperature of the coil is extracted after 0.5 s and visualized in a plot.
左:沉积在线圈中的涡流损失。中心:沉积在线圈中的欧姆损失。右:线圈中的温度分布。L. Bortot,M。Maciejewski,M。Prioli,A.M。的图像Fernandez Navarro,S.Schöps,I。CortesGarcia,B。Auchmann和A.P. Verweij,从他们的Comsol Conference 2016慕尼黑论文中获乐动滚球app下载取。
与线圈温度一起,从模拟结果中提取了线圈电阻和电压。在设计用于超导磁铁的保护系统时,这些值可以用作输入。
线圈的电阻(左)和电阻电压(右)随时间的函数。L. Bortot,M。Maciejewski,M。Prioli,A.M。的图像Fernandez Navarro,S.Schöps,I。CortesGarcia,B。Auchmann和A.P. Verweij,从他们的Comsol Conference 2016慕尼黑论文中获乐动滚球app下载取。
要了解有关该模拟研究的更多信息,请阅读完整的Comsol会议论文:“”乐动滚球app下载超导加速器磁体中电热瞬变的模拟“。有关使用COMSOL多物理学模拟超导体的更多示例,请浏览下面列出的资源。
模拟超导体的其他资源
- 学习关于在YBCO电线中建模超导性
- 探索模拟的使用设计完全超导旋转机器
Oracle和Java是Oracle和/或其分支机构的注册商标。













评论(0)