
When a car hits a pothole, the suspension system can take on major damage in a matter of seconds. Suspension systems must be able to adapt to myriad road conditions while supporting the wheels, seats, and body of the car. To study the performance of a vehicle suspension system, you can use multibody analyses and a simplified lumped model of a mechanical system.
Paving the Way for Innovative Vehicle Suspension Systems
如果有光明的一面击中坑洼怎么办?车辆悬架技术的创新可以使这成为可能。潜在的发展包括一种方法converting kinetic energy into electrical energy to power vehicles,software-driven shocks可以减轻坑洼,并mechanical suspension settings that adjust with voice commands。
如果不先开发强大的基础,就不可能增强悬架系统。毕竟,任何车辆中的悬架系统都需要适应装载变化,吸收道路上的凹陷和颠簸等等。如果没有的话,会出现常见的悬架问题,例如较差的车轮对准,穿弹簧和受损的阻尼器。

带有悬架系统的机箱的一个例子。Christopher Ziemnowicz的图像 - 自己的作品。获得许可CC BY-SA 2.5, viaWikimedia Commons。
By setting up a simplified lumped model in thecomsolMultiphysics®软件,您可以分析和优化车辆悬架系统设计。
在comsolMultiphysics®中建模一个大型机械系统
从ComsolMultiphysics®的5.3a版本开始,可用Lumped Mechanical Systeminterface can be used for modeling discrete mechanical systems in a nongraphical format. This can be in terms of masses, dampers, and springs. You have the option of connecting these systems to a 2D or 3D多体动力学interface. When modeling a lumped mechanical system, you can use both theLumped Mechanical System和多体动力学界面多体动力学模块。
在本教程中,车辆悬架系统的总模型具有三个主要组成部分:
- Wheels
- Seats
- 身体
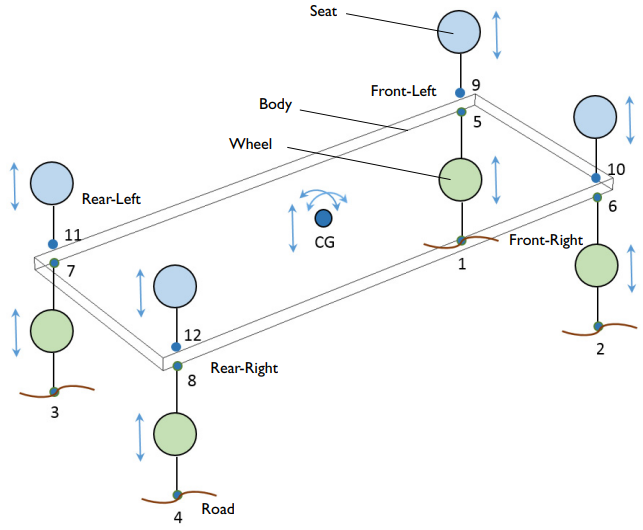
具有三个主要组件的车辆悬架系统的集总模型。
Each wheel has one degree of freedom (DOF) and is represented by a green circle in the image above. Each seat is represented by a blue circle and also has one DOF. At the center of gravity, the body has three DOFs that account for the system’s rotation:
- Roll
- 沥青
- Heave
You can use a刚性域node and规定的位移/旋转子节点在多体动力学interface to restrict the number of DOFs for the body.
To model the wheel and seat, you use the大量的,Spring, 和Damper节点Lumped Mechanical Systeminterface. The full vehicle model includes all four wheels and four seats, and both components are defined as a subsystem.
在下面的示意图中,显示了质量(M),弹簧(K)和阻尼器(C)。车轮的总模型是其质量和刚度,以及车辆悬架的刚度和阻尼。座椅的总模型是其刚度和阻尼以及乘客的质量。
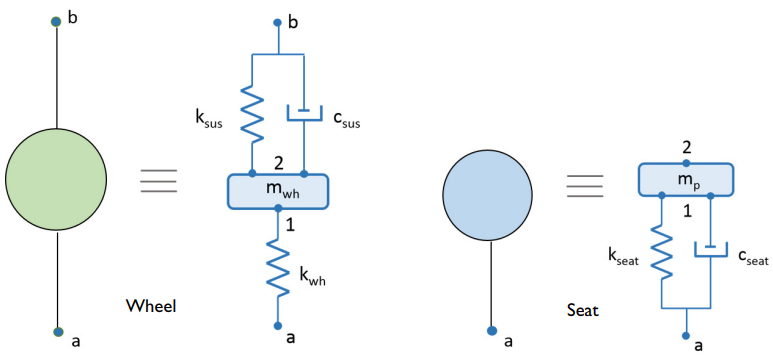
车轮和座椅的总模型。
TheLumped Mechanical System界面使您可以将车身模拟为外部源in the lumped mechanical system. This helps to connect the suspension system with the vehicle body at the wheel-body and body-seat points.
编辑注释在12/13/22:在版本6.1中,刚性域feature has been renamed toRigid Material。
检查瞬态分析结果
通过瞬态分析,您可以在给定的道路轮廓上计算车辆运动和座椅振动水平。在这种情况下,道路的凹凸高度为4厘米,宽度为7.5厘米。假定车辆以40 km/h的恒定速度移动。道路轮廓是通过假设道路上的一系列颠簸来建模的,但假定车辆的左轮轴被假定在颠簸上移动。
Let’s take a look at the time history of the vehicle’s roll, pitch, and heave. These results could be useful for designing shocks that intuitively reduce the amount of roll, pitch, and heave after hitting a pothole.
如下所示,当车辆的左侧在道路轮廓中给出的颠簸上移动时,对于给定的道路激发而言,滚动旋转大于螺距旋转。您还可以在右下方的速度图中看到滚动,音高和升高运动的相应速度。两个不同的频率(低和高)对应于系统组件的固有频率。
Vehicle roll, pitch, and heave motions at the center of gravity (left) and corresponding vehicle velocities (right).
例如,如果您想利用撞击坑洼引起的动能,则需要确定车辆的移动方式及其移动速度。在这种情况下,您可以在所有四个座位位置分析流离失所和加速的时间历史。座椅位移结果表明,车辆的左侧具有更大的位移,因为这侧越过道路的颠簸,而右侧则没有。
座椅位移的时间历史(左)和座椅加速度(右)。
最后,为了确定悬架的柔软或坚硬,并相应地修改了悬架,我们想找出弹簧中的力是什么。结果表明,弹簧的力量幅度和车轮的阻尼器比座椅的力量大得多。这是因为该力被车轮和车身体的惯性吸收,因此只有一小部分力从车轮传输到座椅。此外,与车轮中的力相比,座椅的力的振动频率要低得多,这使得骑行更平滑。
弹簧中的力和前左轮的阻尼器(左)和前左座(右)。
下一步
This simplified model provides a solid foundation for analyzing vehicle suspension, which you can then compare to data from experiments. With verified results, you can enhance suspension system designs for real-world performance.
Try the Lumped Model of a Vehicle Suspension System tutorial yourself via the button above.










Comments (1)
Pavan Kumar
August 29, 2020在应用力子节点中,-lms.e1_f1是什么意思?这是什么?您能描述这是如何变成力量价值的