感应加热
The Induction Heating Process
Induction heating is similar to the焦耳加热效果,但有一个重要的修改。通过电磁诱导诱导加热材料的电流;这是一个非接触式加热过程。

Aninduction coil在导电材料(铜板)上方。
Aninduction coil在导电材料(铜板)上方。
通过将高频交替电流应用于感应线圈,就会产生随时间变化的磁场。要加热的材料,称为workpiece, is placed inside the magnetic field, without touching the coil. Note that not all materials can be heated by induction, only those with high electrical conductivity (such as copper, gold, and aluminum, to name a few). The alternating electromagnetic field induces eddy currents in the workpiece, resulting in resistive losses, which then heat the material up.
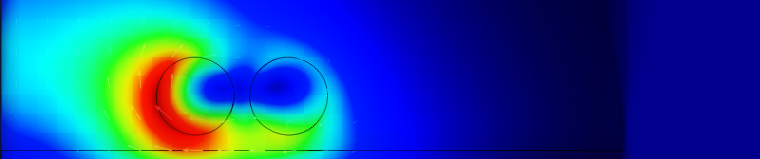
 Induced current density in a copper plate at 10 Hz.
Induced current density in a copper plate at 10 Hz.
Induced current density in a copper plate at 10 Hz.
Induced current density in a copper plate at 10 Hz.
Furthermore, the high frequency leads to a skin effect. The alternating current is forced to flow in a thin layer toward the surface of the workpiece. This in turn leads to an increased resistance of the conductor, ultimately resulting in a greatly increased heating effect.
与其他材料相比,通过诱导更容易加热亚铁金属。这是因为它们的高渗透性增强了诱导的涡流和皮肤效应。另外,发生了另一种加热机制。材料的铁晶体被交替的磁场一遍又一遍地磁化和消除。这会导致磁域快速地来回翻转,从而导致磁滞损失,从而导致额外的热量。
设计中的感应加热
So, induction heating takes place without physical contact between the workpiece and induction coil. This lends it to processes where a high degree of cleanliness is paramount, such as in semiconductor manufacturing, for example.
Additionally, this method of heating is very efficient, as the heat is generatedinside the workpiece, as opposed to somewhere else and then applied to the workpiece. In other words, with induction heating, we can avoid heat losses from the surfaces that would provide the electrical connection, thus improving the overall heating efficiency.
Induction heating involves two different types of physics: electromagnetism and heat transfer. Some material properties are temperature dependent, meaning they change when heat is applied. In that event, you can consider the two physical phenomena coupled.
 Skin effect: The current density is high near the surface of the conductor.
Skin effect: The current density is high near the surface of the conductor.
Skin effect: The current density is high near the surface of the conductor.
Skin effect: The current density is high near the surface of the conductor.
Designs that Leverage Induction Heating
一种利用感应加热的创新是induction stove. In this design, the coil is placed beneath the stove top and its electromagnetic fields act on the metal pot. Since only highly conductive materials can be heated this way, the pot heats up, while if you placed your hand on the stove top, it would not feel hot.
The semiconductor industry also makes use of this process for heating silicon. Other applications include sealing, heat treatment, and welding, to name a few.

Temperature plot:Induction heating in a copper cylinder
Temperature plot:Induction heating in a copper cylinder
When Heating Leads to Wasted Power
尽管由于感应加热,有很多产品和过程能够起作用,但有一乐动体育app无法登录种应用导致浪费的功率。当涉及变压器时,这很重要notto allow eddy currents to flow inside the cores. If eddy currents heat the transformer's magnetic core, power is wasted and further problems could occur, such as structural damage.
Published: November 6, 2014Last modified: February 21, 2017
